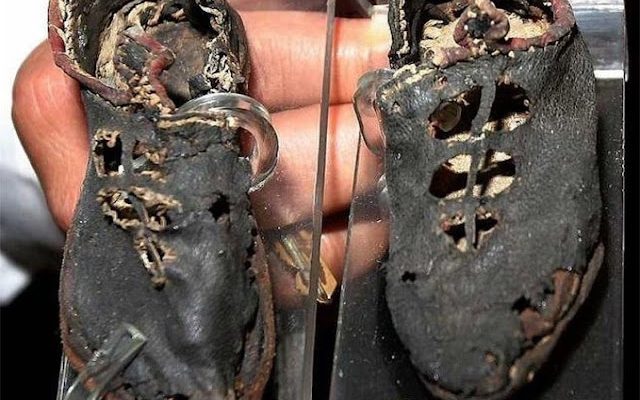
The discovery of a pair of 2,000-year-old Roman children’s shoes in the ruins of Palmyra provides valuable historic context to the ancient city and the broader Roman Empire. Palmyra, located in present-day Syria, was once a flourishing oasis city on the Silk Road, serving as a vital center of trade and culture.
During the Roman period, which spanned from the 1st century BCE to the 3rd century CE, Palmyra enjoyed significant prosperity and emerged as an important regional power. The city thrived under Roman rule, benefiting from its strategic location and favorable economic conditions. Palmyrene merchants engaged in extensive commerce, connecting the Mediterranean world with the East, resulting in the city’s cosmopolitan character and wealth.
The discovery of the children’s shoes offers a glimpse into the daily lives and material culture of the inhabitants of Palmyra during this period.

Shoeswere essential items for both children and adults, providing protection and comfort while traversing the ancient streets and engaging in various activities. By examining the shoes, archaeologists can gain insights into ancient Roman footwear design, materials, and craftsmanship.
Furthermore, the finding of these shoes is a testament to the enduring archaeological significance of Palmyra. The city’s ruins, including the iconic Temple of Bel, the Arch of Triumph, and the Valley of the Tombs, have attracted explorers, scholars, and historians for centuries. Unfortunately, Palmyra has also faced significant threats in recent years due to the ongoing conflict in Syria. The presence of well-preserved artifacts like the Roman children’s shoes highlights the importance of preserving and protecting cultural heritage sites in times of turmoil.
Studying these shoes within the broader historical context of the Roman Empire allows historians to reconstruct aspects of daily life, fashion, and societal norms of the time. It provides valuable evidence of the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations, as well as the lasting influence of Roman culture in regions far beyond the borders of Italy.
In summary, the discovery of 2,000-year-old Roman children’s shoes in the ruins of Palmyra contributes to our understanding of the city’s role in the Roman Empire and offers insights into the material culture and daily lives of its inhabitants. These artifacts provide a tangible connection to the past and underscore the importance of preserving and studying cultural heritage in an ever-changing world.